Backup and restore
You can backup and restore MOSTLY AI just like any other Kubernetes application in your infrastructure by using Velero.
Velero is an open-source tool to backup and restore Kubernetes resources, perform disaster recovery, and migrate Kubernetes cluster resources and persistent volumes. You can also use Velero to snapshot your application state before you perform system operations on your cluster, such as upgrades.
Backup workflow
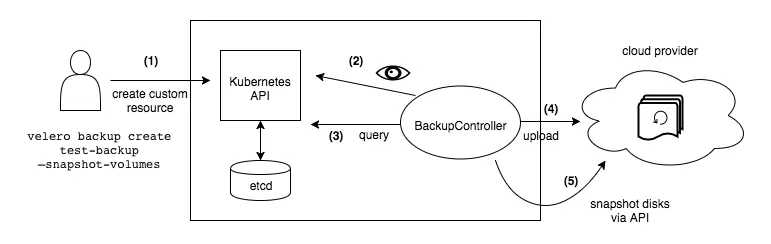
How Velero works?
Each Velero operation – on-demand backup, scheduled backup, restore – is a custom resource, defined with a Kubernetes Custom Resource Definition (CRD) and stored in etcd. Velero also includes controllers that process the custom resources to perform backups, restores, and all related operations.
You can back up or restore all objects in your cluster, or you can filter objects by type, namespace, and/or label.
Set up Velero
Prerequisites
- Access to a Kubernetes cluster, v1.16 or later, with DNS and container networking enabled. For more information on supported Kubernetes versions, see the Velero compatibility matrix on GitHub.
- Install
kubectl. - Identify a storage provider
Velero uses object storage to store backups and associated artifacts. It also optionally integrates with supported block storage systems to snapshot your persistent volumes. Before installing, you should identify the object storage provider and optional block storage provider you want to use. See the list of compatible providers Velero Docs - Providers that Velero supports.
Velero supports storage providers for both cloud-provider environments and on-premises environments. For more details on on-premises scenarios, see the on-premises documentation. - (Optional) To set up Velero CLI autocompletion, see Enabling shell autocompletion from the Velero documentation.
1. Install Velero CLI
Option 1: macOS / Homebrew
On MacOS, you can use Homebrew to install the velero client:
brew install veleroOption 2: GitHub release
- Download the latest release’s tarball for your client platform.
- Extract the tarball:
tar -xvf <RELEASE-TARBALL-NAME>.tar.gz
Move the extracted velero binary to somewhere in your $PATH (/usr/local/bin for most users).
Option 3: Windows - Chocolatey
On Windows, you can use Chocolatey to install the Velero client:
choco install velero2. Deploy Velero Server
There are two supported methods for installing the Velero server components:
-
The
velero installCLI command -
The Helm chart
Note: if your object storage provider is different from your volume snapshot provider, follow the installation instructions for your object storage provider first, then return here and follow the instructions to add your volume snapshot provider.
If you are running MOSTLY AI on-prem, you can use your NFS as a storage destination for backup and restore.
For such cases, see Configuring an NFS Storage Destination*.
*Also configurable in air-gapped environments
3. Install Velero plugins
Velero uses plugins to integrate with a variety of storage systems and Kubernetes platforms to support backup, restore, and snapshot operations. Velero Plugins.
Back up MOSTLY AI
The process below demonstrates the use of Velero to back up storage volumes and all resources for the MOSTLY AI Kubernetes application.
1. Check current namespaces
kubectl get namespacesOutput:
NAME STATUS AGE
default Active 40d
kube-node-lease Active 40d
kube-public Active 40d
kube-system Active 40d
mostly-ai Active 8d
nginx-ingress Active 40d2. Check Velero versions
To do, run:
velero versionOutput:
Client:
Version: v1.12.2
Git commit: -
<error getting server version: no matches for kind "ServerStatusRequest"
in version "velero.io/v1">3. Deploy Velero server on Kubernetes
velero install \
--provider aws \
--plugins velero/velero-plugin-for-aws:v1.8.2,velero/velero-plugin-for-csi:v0.6.2 \
--bucket 453443601263-poc-backup \
--secret-file ./velero_credentials \
--backup-location-config region=eu-central-1 \
--snapshot-location-config region=eu-central-1 \
--use-volume-snapshots=true \
--features=EnableCSI \
--default-volumes-to-fs-backup \
--use-node-agentNOTE: You need to take care on create AWS S3 bucket, for backup destination storage, as well as crate AWS credentials and point it with --secret-file parameter.
Format of velero_credentials file is:
[default]
aws_access_key_id = AKIXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
aws_secret_access_key = 5LBB8XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXCheck Velero versions once again to be sure client and server versions are in sync:
velero versionOutput:
Client:
Version: v1.12.2
Git commit: -
Server:
Version: v1.12.24. Create a backup with Velero
With Velero in palce, you can now create a backup of MOSTLY AI.
Steps
- Initiate the backup with Velero.
velero backup create mostly-ai-backup-poc --include-namespaces mostly-ai - Check the status of the backup and its progress:
You should output similar to the one below.
velero backup describe mostly-ai-backup-pocName: mostly-ai-backup-poc Namespace: velero Labels: velero.io/storage-location=default Annotations: velero.io/resource-timeout=10m0s velero.io/source-cluster-k8s-gitversion=v1.27.8-eks-8cb36c9 velero.io/source-cluster-k8s-major-version=1 velero.io/source-cluster-k8s-minor-version=27+ Phase: InProgress {...} Resources: Included: * Excluded: <none> Cluster-scoped: auto {...} kopia Backups (specify --details for more information): Completed: 1 New: 1
Result
You now have a backup of MOSTLY AI and all related artifacts.
What’s next
You can use velero to get information about the backup
velero backup describe mostly-ai-backup-pocThe backup information should be similar to the one listed below.
Name: mostly-ai-backup-poc
Namespace: velero
Labels: velero.io/storage-location=default
Annotations: velero.io/resource-timeout=10m0s
velero.io/source-cluster-k8s-gitversion=v1.27.8-eks-8cb36c9
velero.io/source-cluster-k8s-major-version=1
velero.io/source-cluster-k8s-minor-version=27+
Phase: CompletedRestore MOSTLY AI from a backup
The process below demonstrates how you can clean up the MOSTLY AI Kubernetes resources and restore MOSTLY AI from a backup.
1. Clean up MOSTLY AI
To restore MOSTLY AI from a backup, make sure that the mostly-ai namespace no longer exists in your cluster.
Steps
- List the Helm releases installed in your cluster.
If you have MOSTLY AI deployed in your cluster, you should see output similar to the one below.
helm listNAME NAMESPACE REVISION UPDATED STATUS CHART APP VERSION mostly-ai mostly-ai 6 2023-12-05 16:11:11.386065 +0100 CET deployed mostly-ai-1.0.0 3.0.0 - Use
helmto uninstall the MOSTLY AI release running in your cluster.If successful, the result from the command should be the following:helm uninstall mostly-airelease "mostly-ai" uninstalled - Delete the
mostly-ainamespace.Output on success:kubectl delete namespace mostly-ainamespace "mostly-ai" deleted - Verify that the
mostly-ainamespace no longer exists.You should see the following:kubectl get all --namespace mostly-aiNo resources found in mostly-ai namespace.
2. Restore MOSTLY AI from a backup
Making sure that the mostly-ai namespace does not exist, you can now restore MOSTLY AI from a backup with Velero.
Steps
- Use
velero restoreto initiate a restore from a backup.
The command below uses themostly-ai-backup-pocbackup that was created in the previous sections and names the restore asmostly-ai-restore-poc.velero restore create mostly-ai-restore-poc --from-backup mostly-ai-backup-poc - Check status of the restore:
The output should be the following:
velero restore describe mostly-ai-restore-pocName: mostly-ai-restore-poc Namespace: velero Labels: <none> Annotations: <none> Phase: InProgress Estimated total items to be restored: 93 Items restored so far: 93 Started: 2023-12-21 08:18:34 +0100 CET Completed: <n/a> Backup: mostly-ai-backup-poc {...} Existing Resource Policy: <none> ItemOperationTimeout: 4h0m0s Preserve Service NodePorts: auto - Check the
mostly-ainamespace:The output should be the following:kubectl get all --namespace mostly-aiNAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE pod/mostly-app-57c86ffc9f-46m9x 1/1 Running 0 84s pod/mostly-coordinator-86c4f9f588-gd4cc 1/1 Running 2 (39s ago) 84s pod/mostly-data-fd7bb94dd-57xcb 1/1 Running 0 84s pod/mostly-keycloak-777b555447-gf5lw 1/1 Running 0 84s pod/mostly-psql-0 1/1 Running 0 84s pod/mostly-ui-864ffb7799-hlq6x 1/1 Running 0 84s pod/replicated-6748579dd9-jbpzq 1/1 Running 0 84s NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE service/mostly-app NodePort 172.20.10.105 <none> 8080:31125/TCP 82s service/mostly-coordinator ClusterIP 172.20.7.60 <none> 8081/TCP 81s service/mostly-data ClusterIP 172.20.206.27 <none> 8000/TCP 81s service/mostly-db ClusterIP 172.20.130.113 <none> 5432/TCP 81s service/mostly-keycloak NodePort 172.20.113.58 <none> 8080:31784/TCP 81s service/mostly-ui NodePort 172.20.5.52 <none> 8888:31465/TCP 81s service/replicated ClusterIP 172.20.165.239 <none> 3000/TCP 81s NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE deployment.apps/mostly-app 1/1 1 1 81s deployment.apps/mostly-coordinator 1/1 1 1 81s deployment.apps/mostly-data 1/1 1 1 80s deployment.apps/mostly-keycloak 1/1 1 1 80s deployment.apps/mostly-ui 1/1 1 1 80s deployment.apps/replicated 1/1 1 1 80s NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE replicaset.apps/mostly-app-57c86ffc9f 1 1 1 83s replicaset.apps/mostly-coordinator-86c4f9f588 1 1 1 83s replicaset.apps/mostly-data-fd7bb94dd 1 1 1 83s replicaset.apps/mostly-keycloak-777b555447 1 1 1 83s replicaset.apps/mostly-ui-864ffb7799 1 1 1 83s replicaset.apps/replicated-57d8f65c98 0 0 0 83s replicaset.apps/replicated-6748579dd9 1 1 1 83s replicaset.apps/replicated-77d9748bd 0 0 0 83s replicaset.apps/replicated-7d4d987ccc 0 0 0 83s replicaset.apps/replicated-7d6c87494c 0 0 0 82s NAME READY AGE statefulset.apps/mostly-psql 1/1 78s - Check the status of the MOSTLY AI pods.
The MOSTLY AI pods should be back and stable.
kubectl get podsNAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE mostly-app-57c86ffc9f-46m9x 1/1 Running 0 2m mostly-coordinator-86c4f9f588-gd4cc 1/1 Running 2 (75s ago) 2m mostly-data-fd7bb94dd-57xcb 1/1 Running 0 2m mostly-keycloak-777b555447-gf5lw 1/1 Running 0 2m mostly-psql-0 1/1 Running 0 2m mostly-ui-864ffb7799-hlq6x 1/1 Running 0 2m replicated-6748579dd9-jbpzq 1/1 Running 0 2m