In this section you will learn more about the following topics:
So let's get started ![]()
This text was created in collaboration with ChatGPT
What is a “Learning Material”
When we talk about Learning Material we refer to any kind of resource used to support learning. This can take many various forms, including online courses, podcasts, books, videos and documentations. The learning materials can be created by instructors, educators, or subject matter experts.
In this section we want to focus on USER-GENERATED learning materials (yes, everyone is invited to create meaningful content) and we will focus on VIDEO and WRITTEN text.
When you have an idea or you want to contribute to a discussion you first need to decide with mode you use. This will depend on several factors including:
-
Learning objective
-
Target audience
-
Information to be communicated
Here’s an overview of which type is better for each situation:
Video:
-
Demonstrating a process
-
Visual demonstrations
-
Engaging learners
-
Complex information
Text:
-
The information is straightforward
-
Convenience to access and review
How to create a new Learning Material
Video:
-
Plan your video
-
Choose the right equipment
-
Keep it engaging
-
Keep it concise
Text:
-
Start with a clear purpose
-
Know your audience
-
Use a clear structure
-
Use simple language
-
Be specific
Tools:
-
Loom
-
Zoom/Google Meet recording
Tools:
-
Confluence
-
Office (PPT, Word…)
-
Google (Docs….)
-
Slack
-
…..
Where to store it
Now that you created the new learning material in the tool of your choice the question is where to store it and how to make it accessible to your target audience.
Two questions might help you:
-
Audience size (small vs. big): is the contribution only relevant for a small group (private chat in Slack with 2 other co-workers) or a larger audience (existing team members & new joiners)
-
Span of relevance (short vs. long): How long will the content be relevant?
The following matrix can support you:
|
Span/Size |
Small |
Big |
|---|---|---|
|
Short |
Choose the tool of your convenience (Confluence, Slack, Docs) |
Choose the tool of your convenience (mainly Slack but also Confluence, Docs….) |
|
Long |
|
|
Hold on - Confluence I understand but why Leapsome - another tool?
![]() Agree we all want to avoid another tool, but to keep it maintainable and relevant for you - the learner - it is important to have a “curated” Learning Management System in place. And I promise it is not that complex and you are using Leapsome for so many other topics already.
Agree we all want to avoid another tool, but to keep it maintainable and relevant for you - the learner - it is important to have a “curated” Learning Management System in place. And I promise it is not that complex and you are using Leapsome for so many other topics already.
![]() Hmm ok tell me more about Leapsome Learning! 👇🏽
Hmm ok tell me more about Leapsome Learning! 👇🏽
How to use Leapsome Learning
There are two options:
Learning elementsAn element is an individual “block” of learning content. |
Learning paths A path is a “journey” made of elements to create a structured and targeted learning experience. |
|---|---|
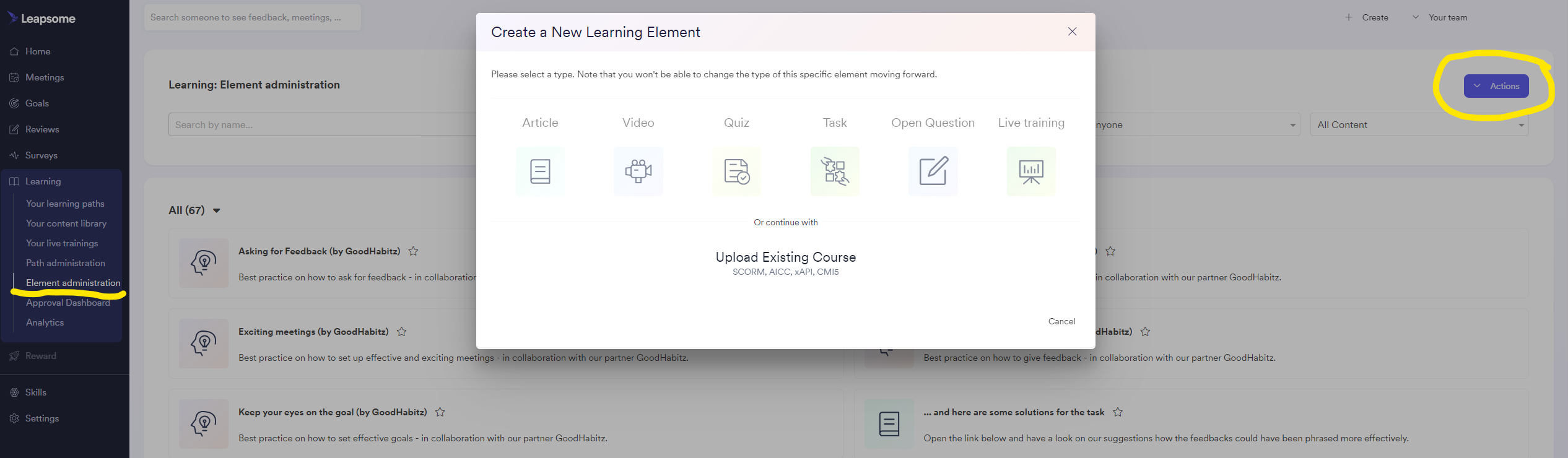
Creating learning elementsGo to Leapsome > Learning (menu on the left) > Element administration > Actions (button on the top right) > + Creating a new learning element
Learning elements can be an article, a video, a task, a quiz, an open-ended question, or an existing course in SCORM, xAPI, AICC or CMI5 format. The maximum size of an upload for a learning element is 5GB. If you recorded your video with Loom, Zoom or Google you only have to add the link to your video and thats all you need to do. Add a meaningful description because the Keyword Search will also use this text. For Zoom recordings please add the Password (if one is required to the description) |
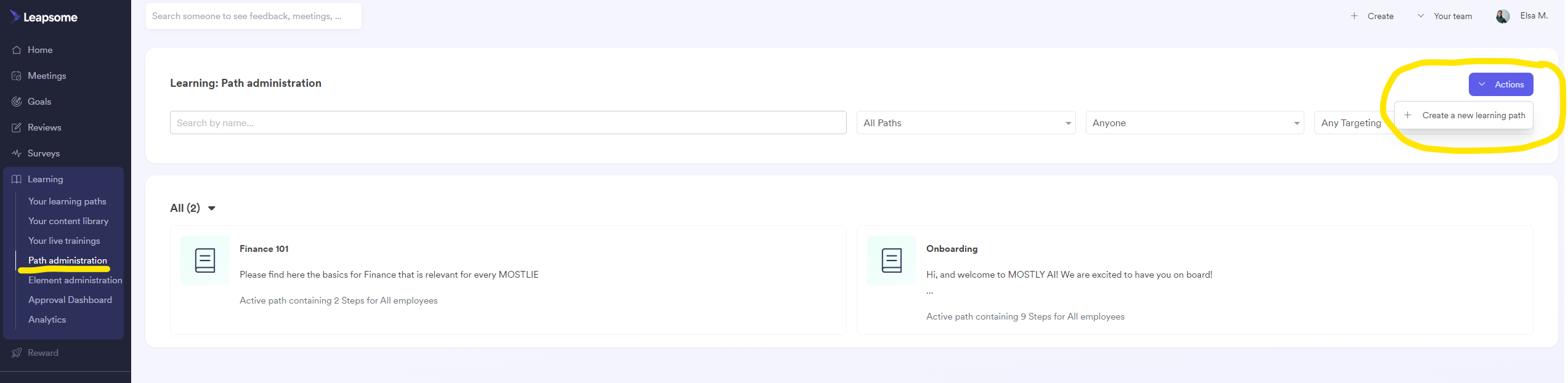
Creating learning pathsGo to Leapsome > Learning (menu on the left) > Path administration > Actions (button on the top right) > + Create a new learning path
Click Save & Continue |
Creating and assigning learning tagsLearning tags can be created to help structure the learning library and categorize the learning content you use. You can add a tag for each learning element. When creating a new learning element, you’ll have the option to choose a tag underneath the description. Tags should be added as the following:
If a new relevant tag doesn’t exist, create a new one: Leapsome > Settings > Admins settings > Learning > scroll to Learning Tags > add it in the Creat new tag box |
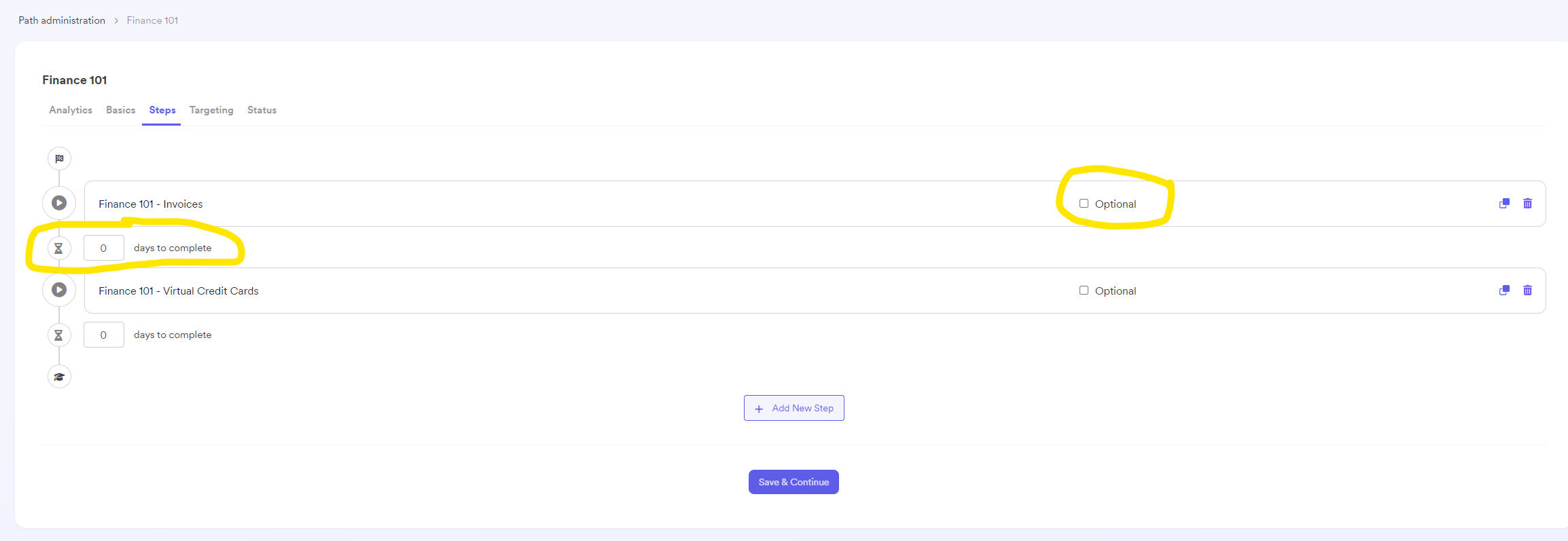
Creating the stepsIt will take you to the next page where you can set up the sequential steps of the learning path. Steps are built using content that can be added by searching through the list of existing learning elements or by uploading new content. Steps can be an article, a video, a task, a quiz, etc Decide if each step is optional (learners can skip it) and define deadlines for each step. The number of days you define each step takes serves as a 'soft' deadline for the users, who will receive a reminder if a step is overdue. If a user misses a deadline, they will be notified but will still be able to complete the step.
Click Save & Continue |
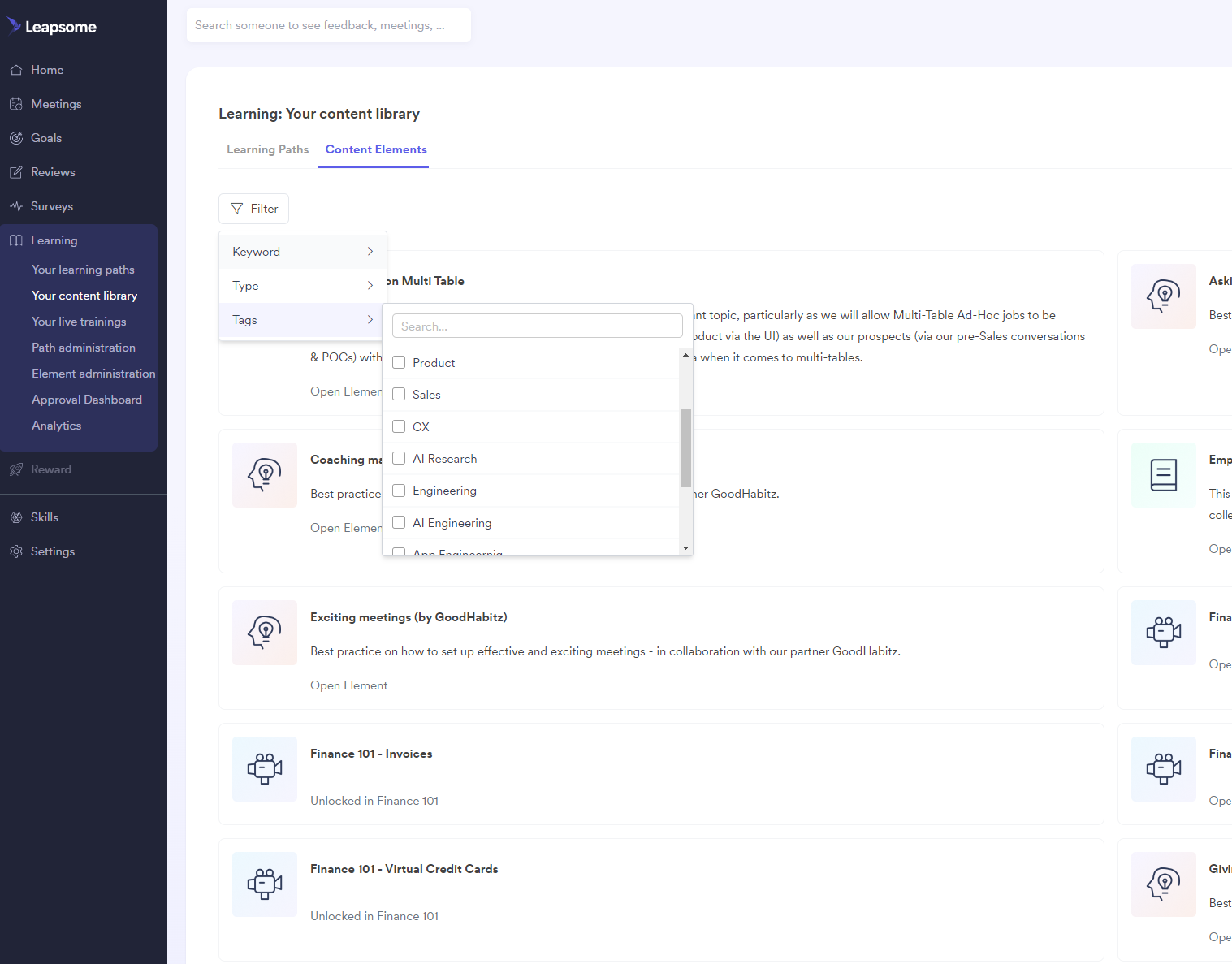
Finding learning elementsGo to Leapsome > Learning (menu on the left) > Your content library > Content elements Then you can scroll or Filter by Tags.
|
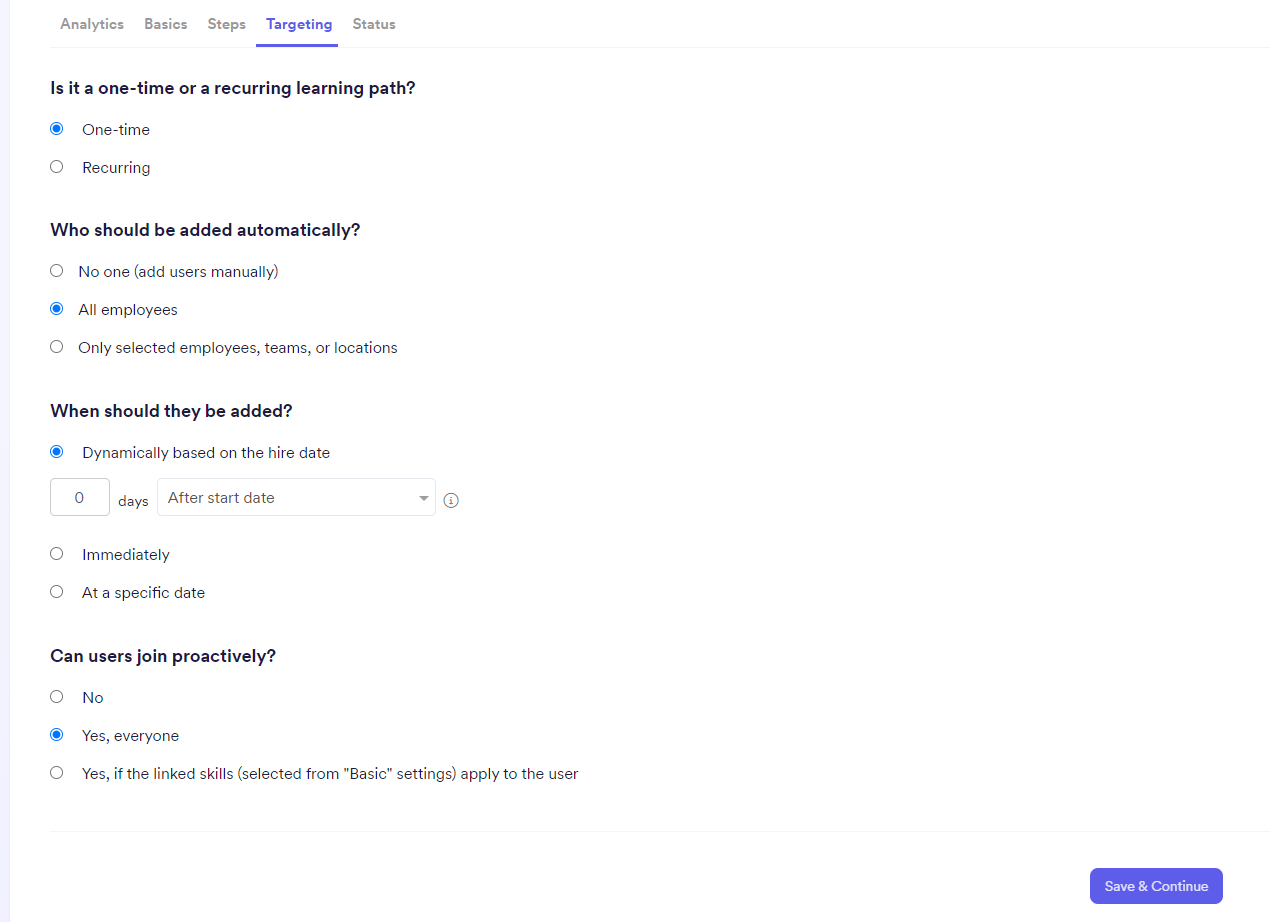
TargetingFinally, you will define who should go through the path and when they should be added.
Please use the targeting feature with extra care. The audience “All employees” should only be used only for special occasions, and after your brainstormed the idea with your Department Lead. |
|
You’re all set! Grab your 🍿 and 🤓 and learn! |
You’re all set! Grab your 🍿 and 🤓 and learn! |
Engage with the learner
We highly recommend to share the link in Slack - the channel depends on the audience, in doubt share it in #mostly-learning or #general. Invite the audience to watch and engage.
Engagement can either happen in the video - eg. when it is a Loom video you can add a comment directly in the video - or outside of the video in the Slack thread.
If you want to keep track of a future discussion you can set up a notification about new replies.
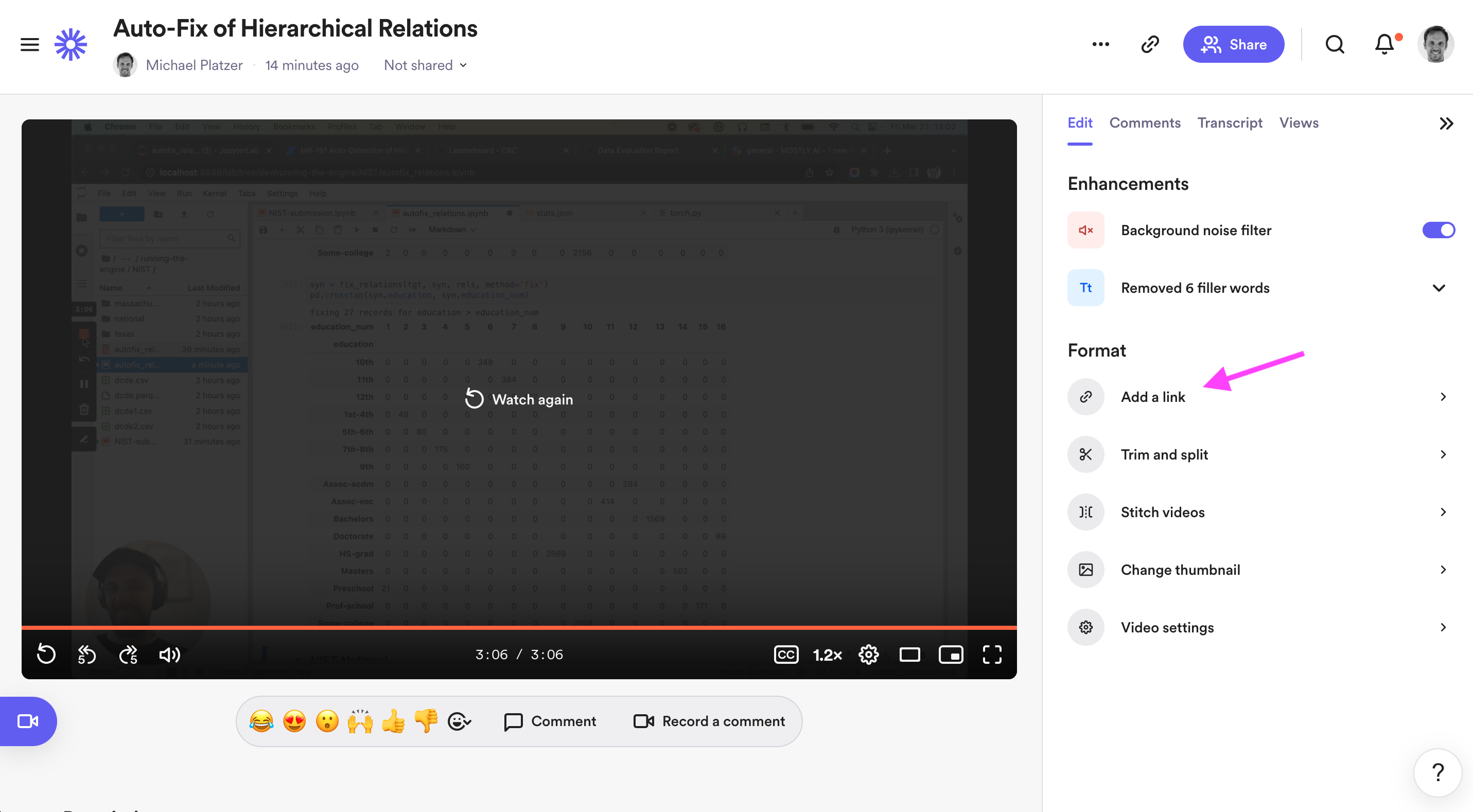
Loom Pro User can add a button with the link to the Slack conversation directly in the video.
If you are not a Pro User you can add the link to the Slack conversation in the description of the Learning Element in Leapsome. This is especially helpful for MOSTLIES joinig later to deep dive into the material.
Keep it relevant
This is the most tricky question and requires - similar to Confluence - all our attention. As a learning material creator it is your responsibility to assess whether the content is still relevant and up to date. The people team will support with the following actions:
-
Conduct regular assessments
-
Provide ongoing training and support
-
Monitor usage and performance
-
Seek feedback from users