Use a MySQL database for synthetic data
MOSTLY AI can use a MySQL database as a source for original data as well as a destination to deliver synthetic data. To do so, you need to create MySQL connectors.
For each MySQL data source or destination, you need a separate connector.
Prerequisites
Obtain the MySQL database connection details.
- host
- port
- database credentials
If you use the web application, create a new MySQL connector from the Connectors page.
Steps
- From the Connectors tab, click New connector.
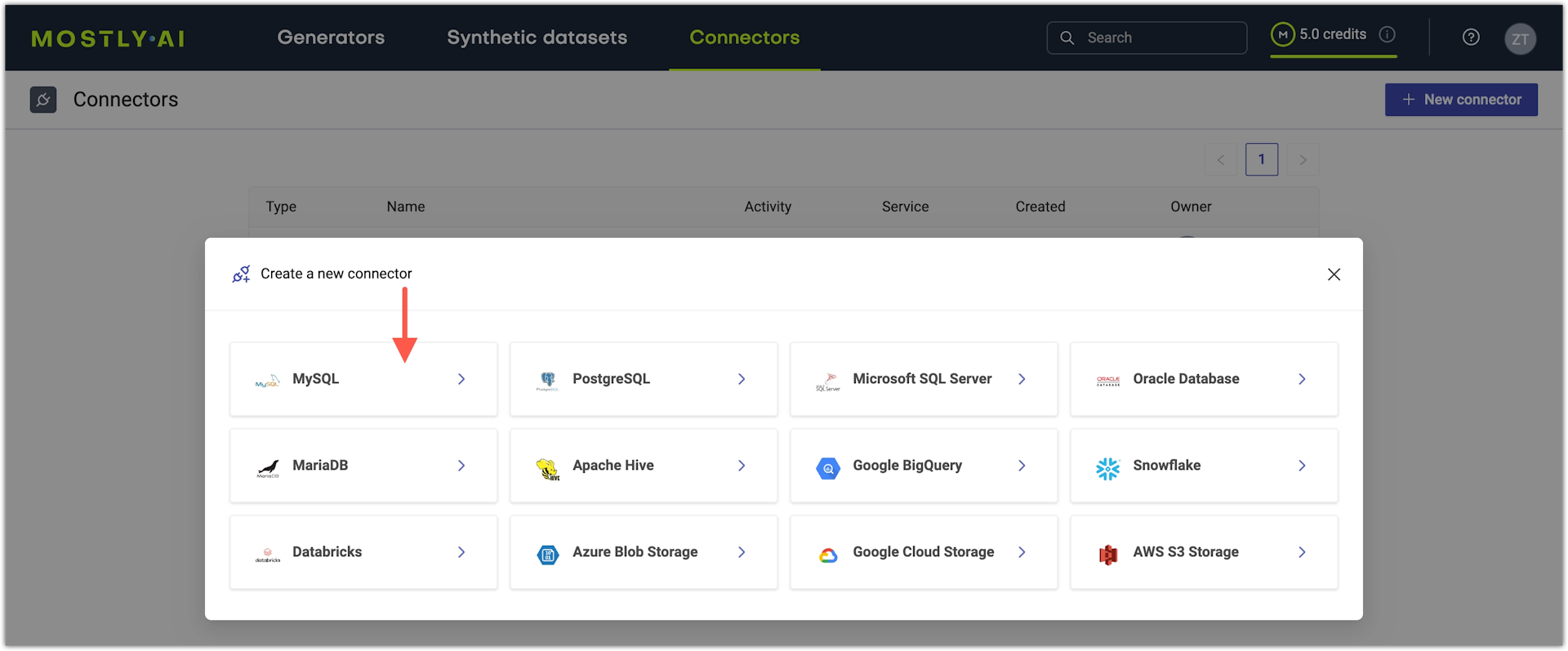
- From the Create a new connector window, select MySQL.
- From the New connector window, configure the connector.
- For Name, enter a name that you can distinguish from other connectors.
- For Access type, select whether you want to use the connector as a source or destination.
- For Host, enter the MySQL database hostname.
- For Port, enter the database port.
The default MySQL port is 3306.
- For Username and Password, enter your MySQL database credentials.
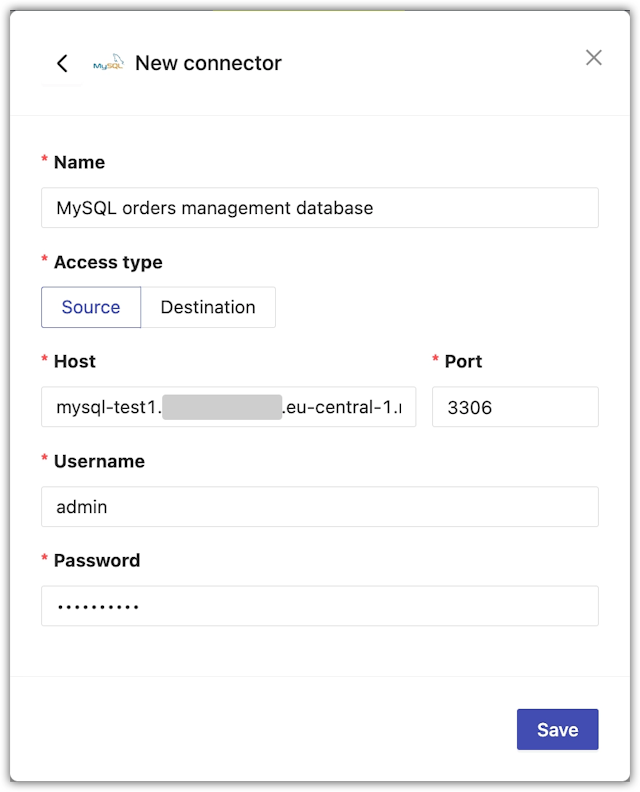
- Click Save to save your new MySQL connector.
MOSTLY AI tests the connection. If you see an error, check the connection details, update them, and click Save again.
You can click Save anyway to save the connector disregarding any errors.
Result
Your connector is now saved.
What’s next
Depending on whether you created a source or a destination connector, you can use the connector as:
- data source for a new generator
- data destination for a new synthetic dataset